Google Cloud Platform is #3 in Top 10 Public Cloud Platforms
Google Cloud Platform is a set of modular cloud-based services that allow you to create anything from simple websites to complex applications. Cloud Platform provides the building blocks so you can quickly develop everything from simple websites to complex applications. Explore how you can make Cloud Platform work for you.
Positions in ratings
#3 in Top 10 Public Cloud Platforms
#3 in Top 10 AI Platforms
Alternatives
The best alternatives to Google Cloud Platform are: Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, Oracle Cloud
Latest news about Google Cloud Platform
2024. Google injects generative AI into its cloud security tools
Google has rolled out a suite of new cloud-based security offerings alongside updates to its existing lineup, targeting enterprises handling extensive, multi-tenant networks. Among these introductions is Gemini in Threat Intelligence, a fresh addition to Google's Mandiant cybersecurity platform, harnessing Gemini's capabilities. Currently available for public preview, Gemini in Threat Intelligence empowers users to analyze significant volumes of potentially malicious code, conduct natural language searches for ongoing threats or signs of compromise, and distill insights from open source intelligence reports across the internet. And in Security Command Center, Google’s enterprise cybersecurity and risk management suite, a new Gemini-driven feature lets security teams search for threats using natural language while providing summaries of misconfigurations, vulnerabilities and possible attack paths.
2022. Google Cloud will shutter its IoT Core service next year
This week, Google Cloud made the announcement that it will be discontinuing its IoT Core service, allowing customers a one-year timeframe to transition to a partner for the management of their IoT devices. Google believes that relying on partners to handle the process on behalf of customers is a more effective approach. A Google spokesperson explained, "Since the launch of IoT Core, it has become evident that our customers' needs can be better met by our network of partners who specialize in IoT applications and services. We have diligently worked to offer customers migration options and alternative solutions, and we are providing a year-long transition period before discontinuing IoT Core."
2022. Google expands Vertex, its managed AI service, with new features
Roughly one year ago, Google introduced Vertex AI, a managed AI platform designed to expedite the deployment of AI models for businesses. Today, Google has announced upcoming enhancements for Vertex, including a dedicated server for AI system training and the introduction of "example-based" explanations. As Google has consistently emphasized, Vertex offers the advantage of integrating Google Cloud services for AI within a unified user interface (UI) and application programming interface (API). According to Google, notable customers such as Ford, Seagate, Wayfair, Cashapp, Cruise, and Lowe's utilize Vertex to construct, train, and deploy machine learning models within a single environment, effectively transitioning from experimental stages to production.
2019. Google Cloud gets a new family of cheaper general-purpose compute instances
Google Cloud has recently introduced its new E2 family of compute instances, specifically designed for general-purpose workloads. These instances offer a significant cost advantage, delivering savings of approximately 31% when compared to the existing N1 general-purpose instances. Moreover, the new system incorporates enhanced intelligence in terms of VM placement, granting the flexibility to migrate them to alternative hosts as required. To achieve these advancements, Google has developed a custom CPU scheduler. Unlike comparable alternatives offered by other cloud providers, E2 VMs from Google can sustain high CPU loads without artificial throttling or complex pricing structures. It will be intriguing to witness benchmark tests that compare the performance of the E2 family against similar offerings from AWS and Azure.
2018. Google Cloud adds new applications performance monitoring tool
Google has introduced a significant addition for developers working on applications within the Google Cloud Platform. They now have access to a comprehensive suite of application performance management tools known as Stackdriver APM. This suite empowers developers to directly track and address issues within the applications they have built, eliminating the need to rely solely on operations teams. The underlying idea is that developers, being intimately familiar with the code, are best positioned to comprehend the signals emanating from it. Stackdriver APM consists of three primary tools: Profiler, Trace, and Debugger. While Trace and Debugger were already available, the integration of Profiler allows all three tools to seamlessly collaborate in identifying, monitoring, and resolving code-related issues.
2018. Google Compute Engine adds simple machine learning service
Google has introduced AutoML, a groundbreaking service available on Google Compute Engine that empowers developers, even those without prior machine learning (ML) expertise, to construct personalized models for image recognition. The scarcity of machine learning experts and data scientists in today's market is widely acknowledged. To address this challenge, Google's new service enables virtually anyone to submit their images, upload them (and import or create tags within the application), and automatically generate a custom machine learning model using Google's advanced systems. The entire process, from data importation to tagging and model training, is facilitated through a user-friendly drag and drop interface. It's important to note that this service goes beyond the capabilities of Microsoft's Azure ML studio, which offers a Yahoo Pipes-like interface for model building, training, and evaluation.
2017. Google Cloud Platform cuts the price of GPUs by up to 36 percent
Google is implementing a price reduction for Nvidia's Tesla GPUs on its Compute Engine service, with savings of up to 36 percent. In U.S. regions, the cost of utilizing the slightly older K80 GPUs has been reduced to $0.45 per hour, while the more advanced and powerful P100 machines will now cost $1.46 per hour, both with per-second billing. By doing so, Google aims to attract developers who seek to execute their own machine learning workloads on its cloud platform. Additionally, various other applications, such as physical simulations and molecular modeling, can greatly benefit from the extensive number of cores provided by these GPUs.
2017. Google Cloud Platform gets a cheaper, lower-performance networking tier
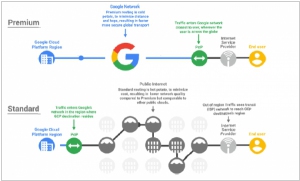
Google is introducing a new networking option for users of its Cloud Platform that offers a more affordable solution. Developers now have the choice between a premium tier, which prioritizes routing traffic over Google's high-speed networks to minimize distance and hops, and a standard tier, which relies on the public internet with potential slowdowns and additional hops. The standard tier is priced 24-33 percent lower than the premium tier in North America and Europe. However, Google applies different pricing models to each tier. The premium tier's pricing is based on the source and destination of the traffic, accounting for the distance it travels over Google's network. In contrast, the standard tier's prices are determined solely by the source location. This new offering provides Cloud Platform users with increased flexibility and cost savings depending on their networking requirements.
2017. Google Cloud Platform improved its free tier

Google has introduced an enhanced always-free tier and trial program for its Cloud Platform. The free tier has been upgraded to provide sufficient resources for running a small application on Google's cloud infrastructure. Users can now utilize a small (f1-micro) instance in Compute Engine, along with free usage of Cloud Pub/Sub, Google Cloud Storage, and Cloud Functions. In total, the free tier encompasses 15 services. Notably, the inclusion of the Compute Engine instance and 5GB of free Cloud Storage usage is a significant update, as these services form the foundation of most cloud applications. Detailed limits and specifications can be found here. This development clearly showcases Google's heightened efforts to compete against AWS by offering a comparable, but more expansive, free tier program to its users.
2017. Google Cloud Platform takes on Windows Azure with new Windows VMs

Today, Google unveiled a range of new offerings designed to entice IT professionals who utilize Windows in their data centers to embrace the Google Cloud Platform. The company introduced support for Microsoft SQL Server Enterprise and Windows Server Core on its Cloud Platform. Additionally, Google announced the inclusion of SQL Server Always-On Availability Group support, addressing the concerns of customers seeking high availability and disaster recovery capabilities for critical operations in a cloud environment. In practical terms, this means that IT professionals can now launch pre-configured virtual machines with any of these products on the Google Cloud Platform and pay for them on a per-minute basis. Alternatively, they have the option to bring their existing SQL Server license, which they have already paid for, and leverage it on the platform.
2017. Google Cloud Platform gets a new key management service
Google Cloud Platform is introducing a new key management service aimed at assisting enterprises, particularly those operating in regulated sectors such as healthcare and banking, in the creation, utilization, rotation, and destruction of their encryption keys in the cloud. Historically, enterprises have managed their keys on-premise; however, as they gradually migrate more of their workloads to the cloud, they have also begun contemplating how to effectively handle their keys in the cloud environment. For instance, Amazon and Microsoft have long provided similar tools with their AWS Key Management Service and Azure Key Vault respectively. Notably, Google itself had already offered a more fundamental version of Cloud KMS, enabling users to provide their own encryption keys.
2016. Google Cloud Platform gets new a cold storage service
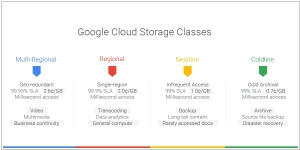
Google has introduced a new cold storage service called Coldline designed for data archiving and disaster recovery purposes. Coldline serves as an alternative to Amazon Glacier, complementing Google Cloud Storage's existing similar service called Nearline. Earlier this year, Nearline transitioned out of its beta phase and underwent significant performance enhancements. Previously, data access experienced a latency of three to five seconds, but after the improvements, it became virtually real-time. Coldline now bridges the gap that was left by the upgraded Nearline service. In terms of pricing, Coldline offers storage at a cost of $0.007 per gigabyte per month, with an additional retrieval fee of $0.05 per gigabyte. In contrast, Nearline is priced at $0.01 per month. While the difference may seem small on an individual basis, the costs can accumulate rapidly for users dealing with substantial amounts of data.
2015. Google launched custom machine types for its Cloud Platform
Google Cloud Platform has introduced a new method of purchasing virtual machines in its cloud called Custom Machine Types. This innovative feature allows users to specify the exact number of vCPUs they require, up to a maximum of 32, as well as the desired amount of memory per vCPU, which can go up to 6.5 GiB (Google prefers the term 'gibibytes' for precision instead of 'gigabyte'). With Custom Machine Types, users have the flexibility to adjust the number of cores and memory according to their evolving needs. For instance, if a virtual machine with two vCPUs is no longer sufficient, rather than upgrading to a machine type with four vCPUs, users can select the optimal configuration, even if it requires only three vCPUs. This eliminates the need to pay for excessive computing power that exceeds actual requirements.
2015. Google Cloud Platform now allows to store Docker container images

Google has recently introduced the beta launch of the Google Container Registry, a service available on its Cloud Platform. This new offering empowers developers to host, share, and manage their private Docker container repositories within Google's cloud computing environment. While Docker provides a public images registry, offering a wide range of preconfigured server packages, some businesses prefer to keep their containers private and not publish them on a public repository. They can either set up their own private repositories or utilize cloud-based services like Quay.io that offer similar functionalities. Similarly, Google's Container Registry operates on the same principle, with a specific focus on integration within Google's cloud computing platform. It enables developers to maintain and manage their Docker container repositories securely within the Google Cloud Platform ecosystem.
2014. Google Cloud Platform now supports server-side software for Windows

Google has introduced Microsoft License Mobility for Google Cloud Platform, enabling its customers to migrate their existing Microsoft server application software licenses (such as SQL Server, SharePoint, Exchange Server, etc.) from on-premises environments to Google Cloud Platform without incurring any additional Microsoft software licensing fees. This advancement simplifies the transition to Google's cloud services and allows customers who prefer perpetual licenses to continue utilizing them. Additionally, as part of this update, Google Compute Engine now offers beta access to Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter Edition for all Google Cloud Platform customers. This option is particularly appealing to enterprises seeking to reduce risk in the cloud and migrate certain workloads from Azure to an alternative platform, in this case, Google Cloud.
2014. Google Cloud Platform slashes prices, adds containers, VPN support

During the recent Google Cloud Platform conference, Google announced several new products and updates for its Google Cloud Platform. One of the highlights is the introduction of Google Container Engine, a service that enables businesses to transition from managing application components on individual virtual machines to utilizing portable Docker containers scheduled within a managed compute cluster. Additionally, App Engine now includes auto-scaling support, Cloud SDK integration, and compatibility with runtimes built on Docker containers. Google also unveiled forthcoming features such as carrier interconnect in partnership with providers like Verizon and VPN support, set to launch in early 2015. These additions allow users to retain certain apps and data on-premises while utilizing the public cloud for other tasks. Moreover, Google has implemented significant price reductions for its Cloud Platform, benefiting businesses of all sizes. In addition to a 10% price reduction last month, the latest cuts include nearly 25% reduction in BigQuery Storage, around 80% reduction in PD Snapshots, nearly 50% reduction in Disk SSD storage, and a 25% drop in the price of large Cloud SQL instances. These pricing adjustments aim to enhance the satisfaction of both large-scale and small-scale business partners.