Cloud Databases Engines
Updated: November 11, 2023
Cloud database engines are specialized software services provided by cloud service providers that allow users to store, retrieve, and manage data in the cloud. These engines are designed to handle the complexities of database management, including provisioning, scaling, replication, backups, and security, so that users can focus on developing applications and analyzing data without worrying about infrastructure maintenance. Cloud database engines come in various types, such as SQL databases for structured data, NoSQL databases for unstructured or semi-structured data, and in-memory databases for ultra-fast data processing. Examples of popular cloud database engines include Amazon RDS, Microsoft Azure SQL Database, Google Cloud SQL, and MongoDB Atlas. These services offer benefits like flexibility, scalability, high availability, and cost-effectiveness, making cloud database engines a vital component in modern cloud-based application development and data management strategies.
Cloud Database Engines - database management systems that run on a cloud computing platforms with high load.
See also: Top 10 Public Cloud Platforms
See also: Top 10 Public Cloud Platforms
2023. Oracle brings its database infrastructure to Microsoft Azure
Oracle has revealed a strategic collaboration with Microsoft, introducing an innovative offering named Oracle Database@Azure, denoted by the use of an "at" symbol for emphasis. This partnership involves hosting a segment of Oracle's infrastructure on the Azure cloud, enabling customers to avail themselves of Oracle database services operating on Oracle hardware within Azure data centers. The synergy aims to combine the strengths of Oracle's database product with the acclaimed "security, flexibility, and best-in-class services" offered by Azure, which includes services developed in collaboration with Microsoft's AI partner, OpenAI. Termed as a move to expand options for Oracle clientele transitioning to the cloud, Oracle Database@Azure promises a "fully integrated" experience for deploying, managing, and utilizing Oracle database instances seamlessly within the Azure environment.
2023. Neon, a relational database startup, lands $45M
Neon, a startup working on a serverless open-source alternative to AWS Aurora Postgres, has recently secured approximately $46 million in a fresh funding round. What sets Neon apart is its innovative architecture that separates storage and compute, resulting in a serverless multi-cloud Postgres database solution. Neon offers several unique features, such as branching, which allows the creation of isolated database instances for testing and development purposes, and point-in-time recovery, enabling the restoration of a database to a specific historical point. Moreover, Neon adopts a cost-effective approach, as it only charges customers for the resources they utilize. The platform optimizes costs by moving infrequently accessed data (cold data) to the most economical storage medium and automatically scaling down to zero during periods of inactivity.
2022. EdgeDB raises $15M ahead of the launch of its cloud database service
EdgeDB, a startup dedicated to modernizing databases for cutting-edge applications, has announced a successful fundraising round of $15 million. The funding will be utilized to launch the previously announced hosted version of EdgeDB's innovative database solution. While EdgeDB's product retains the fundamental aspects of a relational database, it goes beyond conventional concepts, introducing its own high-level data model, a powerful query language known as EdgeQL, a low-latency network protocol, and a comprehensive set of tools for seamless database management, including installation and backup processes. With this investment, EdgeDB aims to propel the evolution of databases, providing developers with an advanced and efficient solution for their modern application needs.
2021. PlanetScale raises $50M for its enterprise database service

The serverless database company, PlanetScale, co-founded by the creators of the Vitess open-source project powering YouTube, has successfully raised $50 million in Series C funding. In addition to this funding milestone, the company has officially announced the general availability of its hosted enterprise platform. Despite initially launching in May 2021 and being limited to private beta, PlanetScale has already attracted notable customers, including YouTube, GitHub, New Relic, Slack, MyFitnessPal, Square, and Affirm. Transactional databases like PlanetScale represent a significant market opportunity within the infrastructure sector. While major cloud providers generate billions from such services, investors have remained cautious.
2021. Yugabyte announces $48M Series C as cloud native database makes enterprise push
Yugabyte, the creator of YugabyteDB, a cloud-native, open-source database, has secured $48 million in funding as the demand for its products continues to grow, particularly among large enterprise customers. The company offers a three-tier solution: the open-source YugabyteDB, a fully managed cloud version called Yugabyte Cloud, and a self-managed cloud version called Yugabyte Platform. The latter option is particularly appealing to large enterprises that prefer to maintain control over their data and infrastructure while operating in the cloud, allowing them to manage their own cloud installations.
2020. PingCAP, the open-source developer behind TiDB, raises $270M
PingCAP, the renowned open-source software developer recognized for its NewSQL database TiDB, has secured a remarkable $270 million in Series D funding. TiDB specializes in handling hybrid transactional and analytical processing (HTAP) and serves as a valuable solution for high-growth companies, particularly in the payment and e-commerce sectors, who grapple with vast volumes of data. Notably, PingCAP highlights that TiDB has been adopted by approximately 1,500 companies worldwide. Prominent examples of its adoption include Square, PayPay (a Japanese mobile payments company), Shopee (an e-commerce app), Dailymotion (a video-sharing platform), and BookMyShow (a ticketing platform).
2020. MariaDB raises $25M more to expand its SkySQL cloud database platform

MariaDB Corporation, the company behind MariaDB SkySQL and a prominent player in the open-source cloud database space, has announced a significant funding round of $25 million. With this latest investment, MariaDB Corp. has now raised a total of over $125 million. The growing demand for database-as-a-service (DBaaS) solutions built on cloud infrastructure and open-source technology has contributed to the success of MariaDB's business. Leading enterprises in various industries, including DBS Bank, ServiceNow, Walgreens, Samsung, and more than 75% of Fortune 500 companies, have chosen MariaDB for their database needs, utilizing both private and public cloud environments. This widespread adoption of the MariaDB platform highlights its versatility and reliability. MariaDB's commitment to open-source principles and its cloud-native approach have positioned it as a trusted provider of DBaaS tools. The funding injection will further strengthen MariaDB's ability to meet the evolving demands of enterprise customers and solidify its position as a leading player in the open-source cloud database market.
2020. MemSQL raises $50M in debt facility for its real-time database platform

MemSQL, the relational database known for its real-time capabilities, enabling organizations to query and analyze vast amounts of rapidly changing data across cloud, hybrid, and on-premise environments, has successfully raised $50 million in funding. Notable customers of MemSQL include major banks, telecommunications carriers, ridesharing giants, and developers working on COVID-19 contact tracing applications. While operating in a competitive landscape that includes industry leaders like Oracle and SAP, MemSQL differentiates itself through its hybrid architecture and remarkable performance. By utilizing innovative technology, MemSQL offers significant speed improvements of approximately 30 times, allowing users to seamlessly process millions of events daily while enabling real-time record querying.
2018. MariaDB acquires big data analytics company MammothDB

MariaDB, which is recognized as a convenient substitute for the widely used MySQL database, is evidently aiming to capture a larger market share and intensify competition against major players such as Oracle and Microsoft SQL Server. In a strategic move, the company has recently acquired MammothDB, a Bulgarian-based service specializing in big data business analytics. MariaDB AX, an existing analytics and data warehousing system offered by MariaDB, will benefit from the expertise of MammothDB in this field. By leveraging MammothDB's knowledge and capabilities, MariaDB aims to enhance the functionality and performance of MariaDB AX.
2016. Microsoft SQL Server is available on Linux
Microsoft's flagship relational database product, SQL Server, has made its debut on Linux with an early private preview, paving the way for a full launch in mid-2017. This development aligns with Microsoft's overarching focus on hybrid deployments, as the company already incorporates Linux into its cloud infrastructure and recently established a significant partnership with Red Hat. In order to ensure the continued relevance of SQL Server, Microsoft recognizes the need to expand its availability across various platforms, even those that were previously considered competitors. Linux, in particular, hosts competing products such as MySQL, MariaDB, and PostgreSQL, which target a similar market segment. By extending SQL Server's reach to Linux, Microsoft embraces the challenge and opportunity to compete in this domain.
2016. MariaDB developer raises $9M

MariaDB Corporation, formerly known as SkySQL and specializing in commercial solutions based on the MariaDB Foundation's SQL fork, has secured an additional $9 million in funding. This funding brings MariaDB's total raised capital to slightly over $40 million. The newly acquired funds will be allocated towards marketing efforts, product launches, and facilitating the company's shift of focus to the U.S. market, departing from its home country of Finland. The foundation acknowledges that the usage of MariaDB has steadily increased since its establishment in October 2011, although a recent sharp decline in the past two months suggests a potential migration by a significant customer. This situation presents an opportunity for MariaDB, as a startup, to capitalize on its widespread usage by offering commercial implementations.
2016. PipelineDB launched Enterprise version of its streaming SQL database

PipelineDB has recently introduced PipelineDB Enterprise, the first commercial iteration of its open-source product that revolutionizes the way SQL databases handle data. Instead of focusing solely on data stored in large silos, PipelineDB adopts a novel approach by considering streams of data. The company has placed a significant bet on this database model, and thus far, it has yielded positive results. Although the exact figures are unavailable, the number of installations is estimated to be in the low thousands, with numerous deployments running continuously throughout the day in the low hundreds. While the commercial version of the product has always been in the pipeline, its release has been expedited due to the increasing demand from large enterprise customers. These customers require additional functionalities such as replication and failover hardware nodes to ensure high availability, particularly for mission-critical applications utilizing the product.
2015. MongoDB broadened its reach to business analysts
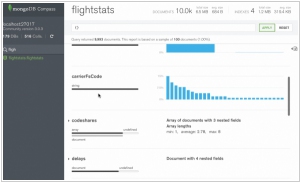
MongoDB, currently ranked as the fourth most popular database globally, has elevated its capabilities with the launch of MongoDB 3.2. With the introduction of MongoDB Connector for BI, business analysts familiar with traditional databases can now seamlessly work with MongoDB using familiar techniques. The steep learning curve that previously posed a challenge has been effectively eliminated. Furthermore, MongoDB is unveiling Compass, a new product that introduces graphical tools comparable to those relied upon by database administrators (DBAs) and development teams in relational databases. Previously, MongoDB users had to sacrifice visibility for flexibility, but this trade-off is no longer necessary. Now, they can effortlessly and securely explore their databases, construct queries visually, inspect records, and make informed decisions regarding their deployments.
2015. IBM buys database-as-a-service provider Compose

IBM has completed the acquisition of Compose, the startup known as MongoHQ that provides a database-as-a-service solution. According to an IBM spokesperson, Compose will continue its regular operations post-acquisition, and existing users will not experience any disruptions. Compose boasts a user base of approximately 3,600 companies spanning various industries, including retail, IoT, and marketing services. So far, users have created over 100,000 databases using Compose's services. Although Compose initially focused on MongoDB databases, it has expanded its offerings to include Elasticsearch, RethinkDB, Redis, and PostgreSQL. The core concept behind Compose is to enable mobile and web developers to build applications without the need to concern themselves with the complexities of their database backends.
2015. Apple acquired NoSQL database engine FoundationDB

Apple has completed the acquisition of FoundationDB, a specialist company renowned for its high-performance, durable NoSQL database solutions. FoundationDB stood out for its impressive ability to handle ACID-compliant transactions at remarkable speeds, while also demonstrating robust scalability. This acquisition appears to be a strategic move by Apple aimed at enhancing its server-side technologies for platforms such as the App Store, iTunes Connect, or iTunes in the Cloud. Given the vast number of applications available in the store and the billions of transactions being served to users, there is undoubtedly room for improvement in these systems. As Apple has sold millions of iPhones, along with a significant number of iPads and Macs, the reliability and speed of its cloud services, particularly iCloud, have become more crucial than ever.
2015. Azure DocumentDB takes on NoSQL databases
Microsoft's Azure DocumentDB, a NoSQL database, will be generally available on April 8. The advantage of these document databases is their ability to directly ingest JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) formatted information, eliminating the need for the mapping process required to transfer data into relational SQL databases. Last year, Amazon Web Services introduced JSON support to its DynamoDB database. As Microsoft aims to equip Azure with a diverse range of workloads, it provides support for various in-house and third-party databases, including MongoDB, Microsoft SQL Azure, and Oracle. Additionally, Microsoft has announced the availability of Azure Search, a "search-as-a-service" that caters to developers seeking to incorporate full-text search functionality into their applications.
2015. NoSQL database Riak gets $25 million investment

Basho, the company responsible for the open-source database and cloud-storage system Riak, has successfully secured a series G funding round of $25 million. In recent years, Basho, alongside MongoDB, DataStax, and Couchbase, has emerged as one of the prominent players in the NoSQL space. Riak, their flagship open-source database, directly competes with Cassandra, which serves as the foundation for DataStax. In 2012, Basho introduced Riak CS, a storage system that enables users to create distributed object stores similar to Amazon Web Services' S3 or OpenStack Swift. While Riak may not have the same user base as MongoDB or the extensive web-scale reputation of Cassandra, there is still significant potential for growth if Basho can improve its operational efficiency and maintain the reliability of its technology. With these factors in place, there should be ample opportunities for success in the market.
2015. Open source database MongoDB raises $80 million

MongoDB, the renowned company recognized for its cutting-edge open source NoSQL database technology, has successfully secured $80 million in funding. MongoDB stands as a prominent contender within the NoSQL database domain, competing against counterparts such as Couchbase and DataStax. The company has been actively exploring avenues to monetize its operations, despite its foundation on open source software. In October, MongoDB introduced the MongoDB Management Service, an innovative solution aimed at assisting users in scaling and managing their databases. The startup anticipates significant revenue generation from this novel service. Furthermore, in August, MongoDB implemented paid support (termed as "production support") for users of the free version, while also appointing a new CEO with expertise in IPOs during the same month.