Hadoop vs IBM Netezza
May 26, 2023 | Author: Michael Stromann
18
The Apache Hadoop software library is a framework that allows for the distributed processing of large data sets across clusters of computers using simple programming models. It is designed to scale up from single servers to thousands of machines, each offering local computation and storage. Rather than rely on hardware to deliver high-availability, the library itself is designed to detect and handle failures at the application layer, so delivering a highly-available service on top of a cluster of computers, each of which may be prone to failures.
2
IBM Netezza appliances - expert integrated systems with built in expertise, integration by design and a simplified user experience. With simple deployment, out-of-the-box optimization, no tuning and minimal on-going maintenance, the IBM PureData System for Analytics has the industry’s fastest time-to-value and lowest total-cost-of-ownership.
Hadoop and IBM Netezza are two distinct data management technologies with different architectures and use cases.
Hadoop is an open-source distributed processing framework designed for handling large volumes of data across a cluster of commodity hardware. It follows a scalable and fault-tolerant approach, using the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) to store data and the MapReduce programming model for processing and analysis. Hadoop is known for its ability to handle unstructured and semi-structured data, making it suitable for big data analytics and batch processing workloads.
IBM Netezza, on the other hand, is an appliance-based data warehouse solution that combines a purpose-built hardware platform with a proprietary database engine optimized for high-performance analytics. It leverages a massively parallel processing (MPP) architecture to deliver fast query performance and data loading capabilities. Netezza is often favored for its simplicity, ease of use, and out-of-the-box analytics functions, making it suitable for organizations seeking quick and efficient data processing without the need for extensive custom coding.
See also: Top 10 Big Data platforms
Hadoop is an open-source distributed processing framework designed for handling large volumes of data across a cluster of commodity hardware. It follows a scalable and fault-tolerant approach, using the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) to store data and the MapReduce programming model for processing and analysis. Hadoop is known for its ability to handle unstructured and semi-structured data, making it suitable for big data analytics and batch processing workloads.
IBM Netezza, on the other hand, is an appliance-based data warehouse solution that combines a purpose-built hardware platform with a proprietary database engine optimized for high-performance analytics. It leverages a massively parallel processing (MPP) architecture to deliver fast query performance and data loading capabilities. Netezza is often favored for its simplicity, ease of use, and out-of-the-box analytics functions, making it suitable for organizations seeking quick and efficient data processing without the need for extensive custom coding.
See also: Top 10 Big Data platforms
Hadoop vs IBM Netezza in our news:
2014. MapR partners with Teradata to reach enterprise customers

The last remaining independent Hadoop provider, MapR, and the prominent big data analytics provider, Teradata, have joined forces to collaborate on integrating their respective products and developing a unified go-to-market strategy. As part of this partnership, Teradata gains the ability to resell MapR software, professional services, and provide customer support. Essentially, Teradata will act as the primary interface for enterprises that utilize or aspire to use both technologies, serving as the representative for MapR. Previously, Teradata had established a close partnership with Hortonworks, but it now extends its collaboration and analytic market leadership to all three major Hadoop providers. Similarly, earlier this week, HP unveiled Vertica for SQL on Hadoop, enabling users to access and analyze data stored in any of the three primary Hadoop distributions—Hortonworks, MapR, and Cloudera.
2014. HP plugs the Vertica analytics platform into Hadoop
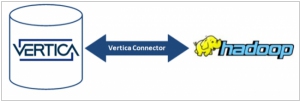
HP has unveiled the introduction of Vertica for SQL on Hadoop, a significant announcement in the world of analytics. With Vertica, customers gain the ability to access and analyze data stored in any of the three primary Hadoop distributions: Hortonworks, MapR, and Cloudera, as well as any combination thereof. Given the uncertainty surrounding the dominance of a particular Hadoop flavor, many large companies opt to utilize all three. HP stands out as one of the pioneering vendors by asserting that "any flavor of Hadoop will do," a sentiment further reinforced by its $50 million investment in Hortonworks, which currently represents the favored Hadoop flavor within HAVEn, HP's analytics stack. HP's announcement not only emphasizes the platform's interoperability but also highlights its capabilities in dealing with data stored in diverse environments such as data lakes or enterprise data hubs. With HP Vertica, organizations gain a seamless solution for exploring and harnessing the value of data stored in the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS). The combination of Vertica's power, speed, and scalability with Hadoop's prowess in handling extensive data sets serves as an enticing proposition, potentially motivating hesitant managers to embrace big data initiatives confidently. HP's comprehensive offering provides a compelling avenue for organizations to unlock the potential of their data, urging them to venture beyond their reservations and embrace the world of big data.
2014. IBM adds Netezza analytics as a service to its cloud
IBM has unveiled a range of new cloud data services for IBM Cloud, expanding its offerings with several innovative tools. These additions include DataWorks, an intelligent data-preparation tool, dashDB, an in-memory analytic database powered by Netezza, and a localized version of the cloud-based database Cloudant. This comprehensive set of capabilities showcases IBM's commitment to enhancing its Bluemix platform. Notably, dashDB positions IBM alongside industry giants like Amazon Web Services, Google, and Microsoft, as it introduces its own analytic service built on columnar database technology, further solidifying its presence in this domain.
2014. The Netezza team is back with Big Data startup Cazena

The recently launched startup Cazena, which secured $8 million in funding, aims to streamline big data processes for large enterprises. Leveraging the expertise of its founding team, who previously worked on the data warehouse specialist Netezza (acquired by IBM in 2010), Cazena is well-positioned to deliver on its promise. Prat Moghe, the CEO of Cazena and former senior vice president at Netezza, is supported by Netezza founder Jit Saxena and longtime Netezza CEO Jim Baum, who both serve on Cazena's board. Cazena recognizes that many large companies face challenges in understanding the necessary technologies for deployment. The complexities surrounding Hadoop, NoSQL, Spark, and Elasticsearch often leave them unsure of when and where to utilize these tools. Moreover, transforming these technologies into a functional "data lake," as advocated by some vendors, proves daunting for these companies. Cazena's approach aims to shift the focus from infrastructure to applications, simplifying the big data landscape. To achieve this, Cazena plans to leverage cloud technology.
2014. Cloudera helps to manage Hadoop on Amazon cloud

Hadoop vendor Cloudera has unveiled a new offering named Director, aimed at simplifying the management of Hadoop clusters on the Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud. Clarke Patterson, Senior Director of Product Marketing, acknowledged the challenges faced by customers in managing Hadoop clusters while maintaining extensive capabilities. He emphasized that there is no difference between the cloud version and the on-premises version of the software. However, the Director interface has been specifically designed to be self-service, incorporating cloud-specific features like instance-tracking. This enables administrators to monitor the cost associated with each cloud instance, ensuring better cost management.