Apache Spark vs MapR
May 18, 2023 | Author: Michael Stromann
5
The MapR Distribution for Apache Hadoop provides organizations with an enterprise-grade distributed data platform to reliably store and process big data. MapR packages a broad set of Apache open source ecosystem projects enabling batch, interactive, or real-time applications. The data platform and the projects are all tied together through an advanced management console to monitor and manage the entire system.
Apache Spark and MapR are both powerful technologies used in big data processing, but they have different roles and characteristics. Apache Spark is an open-source, distributed computing system that focuses on fast data processing and analytics. It provides an in-memory computing framework that enables processing large datasets in real-time with high performance. Spark offers a wide range of libraries and APIs for various tasks like batch processing, machine learning, and graph processing. On the other hand, MapR is a data platform that combines a distributed file system, known as MapR File System (MapR-FS), with additional features for data management and analytics. MapR offers a fully integrated stack that includes Hadoop, Spark, and other components, providing a unified platform for data storage, processing, and analytics. MapR's focus extends beyond Spark to encompass the entire data lifecycle, including data ingestion, storage, governance, and real-time analytics.
See also: Top 10 Big Data platforms
See also: Top 10 Big Data platforms
Apache Spark vs MapR in our news:
2019. HPE acquires big data platform MapR

Hewlett Packard Enterprises (HPE) has completed the acquisition of MapR Technologies, a leading distributor of a data analytics platform based on Hadoop. This strategic deal encompasses the transfer of MapR's technology, intellectual property, and expertise in domains such as AI, machine learning, and analytics data management. By incorporating MapR's portfolio, HPE aims to reinforce its existing offerings in the field of big data, complementing the BlueData software acquisition it made in November. BlueData's software facilitates a container-based approach for deploying and managing Hadoop, Spark, and other environments across bare metal, cloud, or hybrid platforms. The inclusion of the MapR platform brings additional capabilities for running distributed applications, including storage APIs such as S3 API, along with APIs for HDFS, POSIX, NFS, and Kafka.
2015. MapR tries to separate from Hadoop
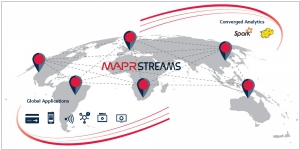
MapR is among the companies operating on the open-source Hadoop platform, facing competition in this domain. To establish a distinctive position among its well-established competitors, MapR has unveiled a new product called MapR Streams. This innovative offering enables the continuous processing of data, allowing for the creation of custom offers by feeding consumer data to advertisers or the distribution of health data to medical professionals to personalize medication and treatment options. These capabilities operate in near real-time, empowering customers to share data sources with individuals or machines that require access to such information through a subscription-based model. For instance, a maintenance program could subscribe to data streams from a manufacturer's shop floor, acquiring insights on usage, production, bottlenecks, and wear and tear. Alternatively, IT departments could subscribe to data streams containing log information, enabling them to detect anomalies that indicate maintenance issues or security breaches.
2015. IBM bets on big data Apache Spark project

IBM has made a significant announcement regarding its involvement in the open source big data project Apache Spark. The company plans to allocate a team of 3,500 researchers to this initiative. Additionally, IBM has unveiled its decision to open source its own IBM SystemML machine learning technology. These strategic moves are aimed at positioning IBM as a frontrunner in the domains of big data and machine learning. Cloud, big data, analytics, and security form the pillars of IBM's transformation strategy. In conjunction with this announcement, IBM has committed to integrating Spark into its core analytics products and partnering with Databricks, the commercial entity established to support the open source Spark project. IBM's participation in these endeavors goes beyond mere altruism. By actively engaging with the open source community, IBM aims to establish itself as a trusted contributor in the realm of big data. This, in turn, enhances its credibility among companies working on big data and machine learning projects using open source tools. The collaborative involvement with the community opens doors for IBM to offer consulting services and seize other business opportunities in this space.
2015. MapR adds Apache Drill to its Hadoop distribution

MapR has recently announced that its Hadoop distribution now includes Apache Drill, an open-source SQL query engine designed for Hadoop and NoSQL environments. Apache Drill offers low-latency capabilities, making it easier for end users to interact with diverse data sources, including legacy transactional systems, Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, web click-streams, and semi-structured data. Furthermore, it provides compatibility with popular business intelligence (BI) and data visualization tools. The inclusion of Apache Drill 1.0 in MapR's distribution grants users free access to this powerful tool. As a result, competitors like Hortonworks, who have contributors involved in the Apache Drill project, can also consider incorporating it into their own distribution if they find it valuable.
2015. MapR revamps its Hadoop platform with more real-time analytics

The most recent version of the enterprise-grade distributed Hadoop data platform MapR is specifically designed for the modern data-centric enterprise, emphasizing real-time capabilities. Its advanced features include table replication, which enables the simultaneous updating of multiple instances in different locations while ensuring synchronized changes across them. The ability to respond promptly to real-time business needs and offer the right solutions is crucial. Failure to do so not only means missed opportunities but can also pose a threat to a company's sustainability. This is one of the reasons why some enterprises are opting for MapR instead of traditional relational database management systems (RDBMS). MapR provides a comprehensive solution that combines a highly regarded NoSQL database and Hadoop in a convenient package. Unlike competitors such as Hortonworks and Cloudera, MapR stands out as a software company focused on simplifying the implementation of big data solutions, making it more accessible and user-friendly.
2015. Google partners with Cloudera to bring Cloud Dataflow to Apache Spark
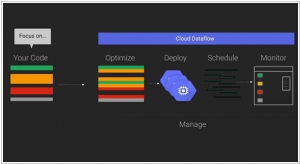
Google has announced a collaboration with Cloudera, the Hadoop specialists, to integrate its Cloud Dataflow programming model into Apache's Spark data processing engine. By bringing Cloud Dataflow to Spark, developers gain the ability to create and monitor data processing pipelines without the need to manage the underlying data processing cluster. This service originated from Google's internal tools for processing large datasets at a massive scale on the internet. However, not all data processing tasks are identical, and sometimes it becomes necessary to run tasks in different environments such as the cloud, on-premises, or on various processing engines. With Cloud Dataflow, data analysts can utilize the same system to create pipelines, regardless of the underlying architecture they choose to deploy them on.
2014. MapR partners with Teradata to reach enterprise customers

The last remaining independent Hadoop provider, MapR, and the prominent big data analytics provider, Teradata, have joined forces to collaborate on integrating their respective products and developing a unified go-to-market strategy. As part of this partnership, Teradata gains the ability to resell MapR software, professional services, and provide customer support. Essentially, Teradata will act as the primary interface for enterprises that utilize or aspire to use both technologies, serving as the representative for MapR. Previously, Teradata had established a close partnership with Hortonworks, but it now extends its collaboration and analytic market leadership to all three major Hadoop providers. Similarly, earlier this week, HP unveiled Vertica for SQL on Hadoop, enabling users to access and analyze data stored in any of the three primary Hadoop distributions—Hortonworks, MapR, and Cloudera.